2026 EITC: Boost Your Refund Up to $7,430

Anúncios
The 2026 Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) provides a vital financial boost for eligible low to moderate-income workers and families, potentially increasing their tax refund by up to $7,430.
Anúncios
Are you ready to significantly boost your tax refund in 2026? The 2026 Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) stands as one of the most powerful tools available to low and moderate-income individuals and families, offering a chance to receive up to $7,430 back. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know to claim this valuable credit and maximize your financial return.
Understanding the 2026 Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC)
The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) is a refundable tax credit for low to moderate-income working individuals and families. It is designed to offset federal payroll and income taxes, providing a substantial financial boost to those who need it most. Unlike a deduction, which only reduces taxable income, a refundable credit can result in a refund even if you owe no tax.
Anúncios
For the 2026 tax year, the EITC parameters have been adjusted to reflect inflation and economic changes, making it crucial to understand the updated eligibility requirements and maximum credit amounts. This credit is not just a simple refund; it’s an investment in American working families, stimulating local economies and providing a safety net.
What is the EITC and How Does It Work?
The EITC is calculated based on your income, filing status, and the number of qualifying children you have. The more qualifying children you have, the higher your potential credit. However, there are strict income limits that must be met. The credit phases in as your income increases, reaches a maximum, and then phases out as your income continues to rise.
- Refundable Credit: Even if you owe no tax, you can still receive the EITC as a refund.
- Income-Based: Eligibility and the amount of the credit depend on your earned income.
- Family-Oriented: Higher credits are available for families with qualifying children.
- Annual Adjustment: Income thresholds and maximum credit amounts are adjusted for inflation each year.
Understanding these fundamental aspects is the first step toward claiming your rightful credit. Many eligible individuals and families often miss out on the EITC simply because they are unaware of its existence or mistakenly believe they don’t qualify. Don’t let that be you; this guide is here to ensure you’re fully informed.
Eligibility Requirements for the 2026 EITC
Qualifying for the 2026 EITC involves meeting several specific criteria set by the IRS. These requirements ensure the credit reaches its intended beneficiaries: low to moderate-income workers and their families. It’s essential to review these carefully, as even minor discrepancies can affect your eligibility or the amount of credit you receive.
The IRS regularly updates these rules, and remaining informed is key to a successful claim. The requirements generally revolve around your earned income, Adjusted Gross Income (AGI), filing status, and the presence of qualifying children.
Key Criteria to Qualify
To be eligible for the 2026 EITC, you must meet all of the following conditions:
- Earned Income: You must have earned income from employment or self-employment. This includes wages, salaries, tips, and other taxable employee compensation, as well as net earnings from self-employment.
- Adjusted Gross Income (AGI): Your AGI must be below certain limits, which vary based on your filing status and the number of qualifying children. For 2026, these limits will be adjusted for inflation.
- Investment Income: Your investment income must be below a specified threshold. For 2026, this threshold will likely be around $11,000.
- Social Security Number (SSN): You, your spouse (if filing jointly), and any qualifying children must have valid SSNs issued before the due date of your 2026 tax return (including extensions).
- Filing Status: You cannot use the “Married Filing Separately” status. You must file as Single, Head of Household, Qualifying Widow(er), or Married Filing Jointly.
- Residency: You must be a U.S. citizen or resident alien all year. If you are a nonresident alien, you must be married to a U.S. citizen or resident alien and choose to be treated as a resident for tax purposes.
- Foreign Earned Income Exclusion: You cannot claim the foreign earned income exclusion.
It’s important to note that even if you don’t have a qualifying child, you might still be eligible for a smaller EITC if you meet the other requirements and are within the age range of 25 to 64 at the end of the tax year. Each of these criteria plays a vital role in determining your eligibility, so take the time to verify each point for your specific situation.
Maximizing Your 2026 EITC Refund: Strategies and Tips
Knowing you’re eligible is one thing, but actively working to maximize your 2026 EITC refund is another. There are several proactive steps you can take throughout the year and during tax season to ensure you receive the largest possible credit. These strategies often involve careful financial planning and accurate record-keeping.
Small adjustments to your income or understanding specific tax rules can lead to a significant increase in your refund. Don’t leave money on the table; explore these tips to boost your EITC.
Key Strategies for a Larger Refund
Maximizing your EITC often comes down to understanding how your income and family situation interact with the credit’s calculations. Here are some effective strategies:
- Accurate Income Reporting: Ensure all earned income, including wages, self-employment income, and tips, is accurately reported. Overlooking income can lead to a lower credit or even an audit. Conversely, failing to report all eligible earned income can also reduce your credit.
- Qualifying Child Rules: Understand the rules for qualifying children. A child must meet age, residency, relationship, and joint return tests. If you have a child who lives with you for more than half the year and meets the other criteria, they are likely a qualifying child.
- Consider Filing Jointly: If you are married, filing jointly often allows for a higher AGI limit for the EITC, potentially qualifying you for a larger credit than if you filed separately (which generally disqualifies you).
- Review Your AGI: Your Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) is crucial. Certain deductions, like contributions to traditional IRAs or student loan interest, can lower your AGI, which might push you into a more favorable EITC bracket or increase your credit amount.
- Avoid Investment Income Limits: Keep a close eye on your investment income. If it exceeds the annual threshold (e.g., around $11,000 for 2026), you become ineligible for the EITC, regardless of your earned income.
By actively managing your financial situation and understanding these strategies, you can significantly enhance your chances of receiving the maximum 2026 EITC. It requires foresight and attention to detail, but the potential reward is well worth the effort.
Important Changes and Updates for the 2026 EITC
The landscape of tax credits is dynamic, with adjustments made annually to reflect economic conditions and legislative changes. For the 2026 tax year, taxpayers should be aware of any new updates or modifications to the EITC that could impact their eligibility or the amount of credit they receive. Staying informed about these changes is crucial for accurate tax filing.
While major legislative overhauls are less frequent, annual inflation adjustments to income thresholds and credit amounts are standard. These adjustments are designed to keep the EITC relevant and effective in supporting low to moderate-income individuals and families.
Anticipated Adjustments and What They Mean
Here’s what to expect regarding changes and updates for the 2026 EITC:
- Inflation Adjustments: The most consistent change year-to-year involves inflation adjustments to the maximum credit amounts and the income thresholds for eligibility. These adjustments typically increase both the maximum credit and the income limits, allowing more people to qualify or receive a larger credit.
- Potential Legislative Revisions: While not guaranteed, Congress could introduce new legislation that impacts the EITC. These changes could range from temporary expansions (as seen during the pandemic) to more permanent structural modifications. Always check official IRS publications or consult a tax professional for the latest legislative updates.
- Increased Awareness Campaigns: The IRS and various non-profit organizations often ramp up awareness campaigns for the EITC, especially when there are significant changes or when many eligible taxpayers are missing out. Pay attention to these campaigns for valuable information.
For 2026, it’s projected that the maximum EITC for those with three or more qualifying children could reach approximately $7,430, with lower amounts for those with fewer or no children. Income limits will also see a bump, likely allowing individuals without children to earn up to around $18,000 and those with three or more children up to about $63,000, while still qualifying. These figures are estimates and will be finalized by the IRS closer to the tax season. Always refer to the official IRS guidance for the most accurate and up-to-date information.
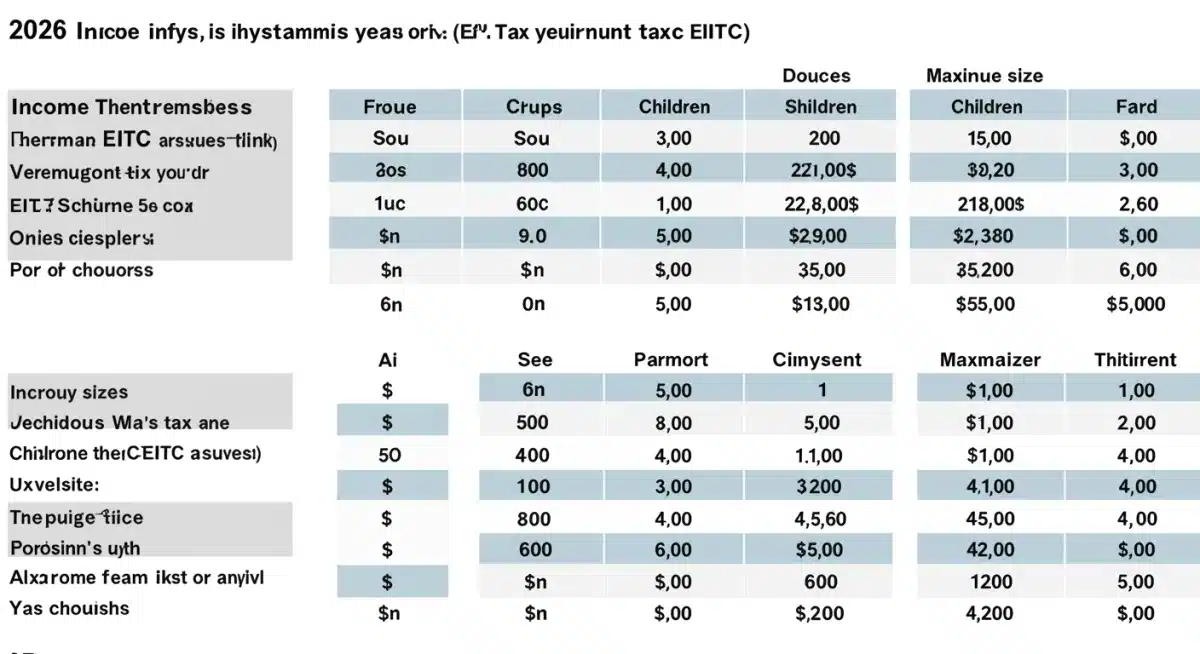
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Claiming the EITC
Despite its significant benefits, many eligible taxpayers either fail to claim the EITC or make errors that lead to delays or reductions in their refund. Avoiding these common pitfalls is crucial for a smooth and successful claim. Accuracy and attention to detail are paramount when dealing with tax credits.
The IRS scrutinizes EITC claims closely due to the potential for errors, so understanding where mistakes typically occur can help you navigate the process effectively and secure your maximum refund without unnecessary complications.
Pitfalls That Can Affect Your EITC
Being aware of these common mistakes can save you time and frustration:
- Incorrectly Claiming a Qualifying Child: This is one of the most frequent errors. Ensure your child meets all four tests: relationship, age, residency, and joint return. For instance, a child must live with you for more than half the year.
- Miscalculating Earned Income: Not all income counts as earned income for EITC purposes. For example, welfare benefits, unemployment compensation, and child support are not earned income. Only wages, salaries, tips, and net earnings from self-employment qualify.
- Filing Status Errors: Using the wrong filing status, especially “Married Filing Separately,” will disqualify you from the EITC. If you are married, filing jointly is almost always the best option for EITC eligibility.
- Errors in Social Security Numbers: Missing or incorrect SSNs for you, your spouse, or your qualifying children can cause your EITC claim to be denied or delayed. Ensure all SSNs are valid and correctly entered.
- Not Claiming the EITC: Perhaps the biggest mistake is simply not claiming the credit. Many eligible individuals, particularly those without qualifying children, are unaware they could receive a credit.
- Ignoring Investment Income Thresholds: Failing to track investment income can lead to unexpected ineligibility. If your investment income (e.g., from dividends, interest, or capital gains) exceeds the annual limit, you cannot claim the EITC.
By meticulously checking all your information and understanding the nuances of these rules, you can significantly reduce the risk of errors and ensure your EITC claim is processed efficiently, helping you get your refund faster.
The Economic Impact of the EITC in 2026
Beyond individual financial benefits, the Earned Income Tax Credit plays a significant role in the broader U.S. economy. It is recognized as one of the most effective anti-poverty programs, lifting millions of people out of poverty annually and providing a crucial boost to local economies. Understanding this wider impact helps contextualize the importance of the EITC.
The funds injected into communities through EITC refunds often go directly back into local businesses, supporting consumer spending and economic growth. This ripple effect benefits not only the recipients but also their communities and the national economy as a whole.
EITC’s Role in Poverty Reduction and Economic Growth
The EITC’s design makes it a powerful tool for economic and social welfare:
- Poverty Reduction: Studies consistently show that the EITC is a primary driver in reducing poverty, especially among families with children. It encourages work by supplementing the earnings of low-income workers rather than replacing them.
- Economic Stimulus: Recipients typically spend their refunds on essential needs like housing, food, transportation, and education. This spending directly stimulates local economies, supporting businesses and creating jobs.
- Improved Child Outcomes: Research indicates that children in families receiving the EITC tend to have better health, educational, and long-term earnings outcomes. The financial stability provided by the credit allows families to invest more in their children’s well-being.
- Work Incentive: Unlike some other welfare programs, the EITC is designed to encourage work. As earned income increases, so does the credit, up to a certain point, incentivizing individuals to seek and maintain employment.
In 2026, as economic conditions continue to evolve, the EITC will remain a vital component of the nation’s economic support system. Its ability to provide direct financial assistance, reduce poverty, and stimulate local economies underscores its importance far beyond individual tax returns. Ensuring eligible individuals claim this credit is not just a personal gain but a societal benefit.
Resources and Assistance for Claiming Your 2026 EITC
Navigating tax laws and claiming credits like the EITC can seem daunting, but you don’t have to do it alone. Numerous resources and assistance programs are available to help you understand your eligibility, prepare your tax return, and ensure you receive your maximum 2026 EITC refund. Leveraging these resources can make the process much smoother and more accurate.
From free tax preparation services to official IRS guidance, knowing where to turn for help is invaluable. Don’t hesitate to seek assistance if you’re unsure about any aspect of claiming your EITC.
Where to Find Help and Information
Here are some reliable sources for assistance with your 2026 EITC claim:
- IRS.gov: The official IRS website is the primary source for all EITC information, including updated income thresholds, eligibility rules, and forms. They also have an EITC Assistant tool to help you determine if you qualify.
- Volunteer Income Tax Assistance (VITA) and Tax Counseling for the Elderly (TCE): These IRS-sponsored programs offer free tax help to qualified individuals, including those with low to moderate income, persons with disabilities, the elderly, and limited English-speaking taxpayers. Certified volunteers provide free basic income tax return preparation.
- Tax Software: Many tax preparation software programs (both free and paid) can guide you through the EITC eligibility questions and calculate your credit automatically. Look for reputable software that offers clear explanations.
- Tax Professionals: If your tax situation is complex, or you prefer personalized assistance, a qualified tax professional (e.g., a CPA or Enrolled Agent) can help ensure you claim all eligible credits and deductions, including the EITC.
- Community Organizations: Many local community centers, non-profits, and financial literacy organizations offer workshops or one-on-one assistance to help residents understand and claim tax credits like the EITC.
Utilizing these resources can significantly increase your confidence in filing your tax return and maximize your chances of receiving the full 2026 EITC you are entitled to. Proactive engagement with these tools and services is a smart financial move for any eligible taxpayer.
| Key Aspect | Description for 2026 EITC |
|---|---|
| Maximum Refund | Up to $7,430 for families with 3+ qualifying children (est.). |
| Eligibility Focus | Low to moderate-income workers and families, based on earned income and AGI. |
| Key Requirement | Valid SSNs for all claimants and no ‘Married Filing Separately’ status. |
| Maximization Tip | Accurate income reporting and understanding qualifying child rules are crucial. |
Frequently Asked Questions About the 2026 EITC
For the 2026 tax year, the estimated maximum Earned Income Tax Credit is around $7,430, applicable to families with three or more qualifying children. The exact amount depends on your income, filing status, and the number of children you claim.
No, you do not necessarily need children to qualify for the 2026 EITC. Individuals without qualifying children can also be eligible, though the maximum credit amount is significantly lower. You must be between 25 and 64 years old at the end of the tax year.
Earned income for EITC purposes primarily includes wages, salaries, tips, and other taxable employee compensation, as well as net earnings from self-employment. Unemployment benefits, child support, and pensions generally do not count as earned income.
The EITC has specific income limits that vary by filing status and the number of qualifying children. If your Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) or investment income exceeds these thresholds for 2026, you will not be eligible for the credit. These limits are adjusted annually for inflation.
You can find free tax preparation assistance through IRS-sponsored programs like Volunteer Income Tax Assistance (VITA) and Tax Counseling for the Elderly (TCE). These programs offer certified volunteers who can help eligible taxpayers prepare their returns accurately and claim the EITC.
Conclusion
The 2026 Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) offers a substantial financial opportunity for eligible low to moderate-income Americans, with the potential to boost refunds by up to $7,430. By understanding the eligibility requirements, leveraging strategies to maximize your credit, avoiding common errors, and utilizing available resources, you can confidently navigate the tax season. The EITC is more than just a tax break; it’s a critical tool for financial stability, poverty reduction, and economic growth. Don’t miss out on this valuable credit – ensure you’re fully prepared to claim your rightful refund.






